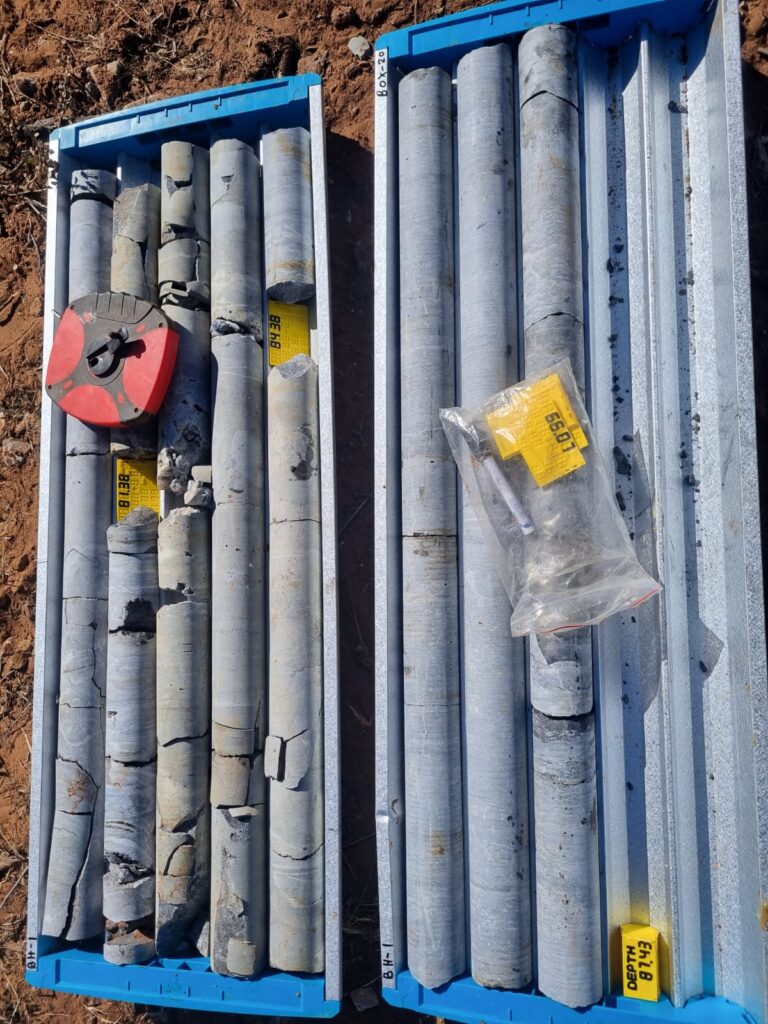
Our Expertise
Comprehensive Drilling Services for Your Needs
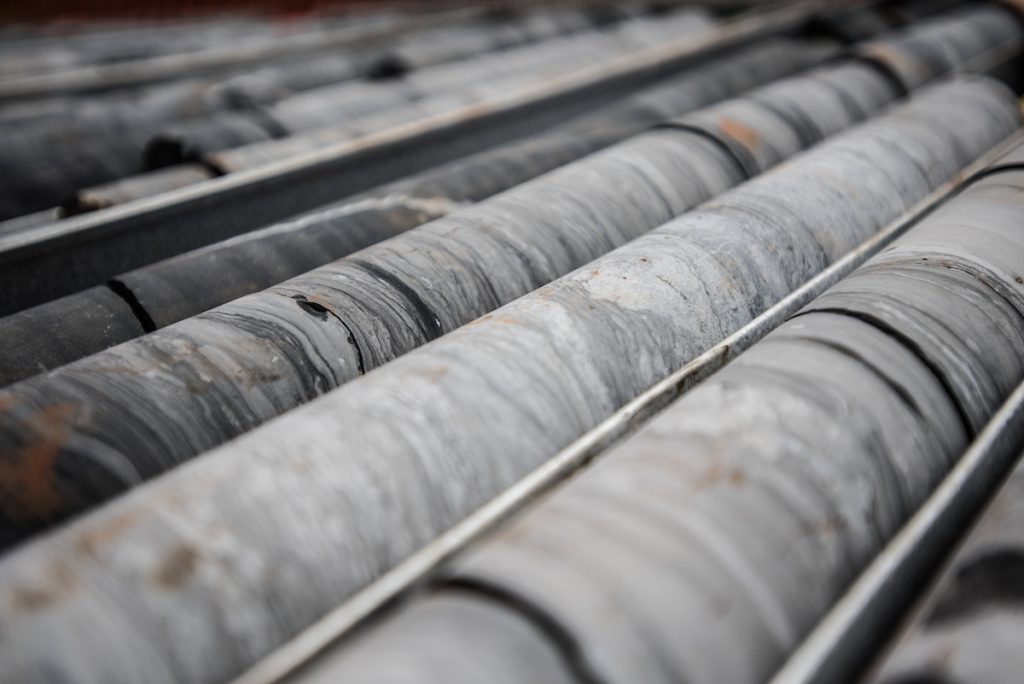

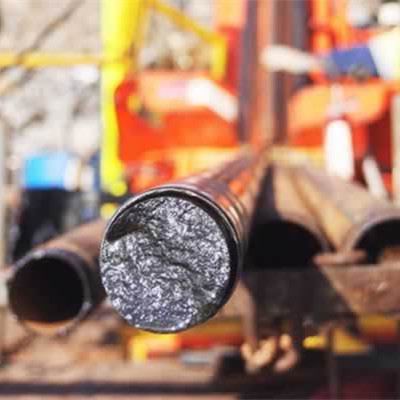
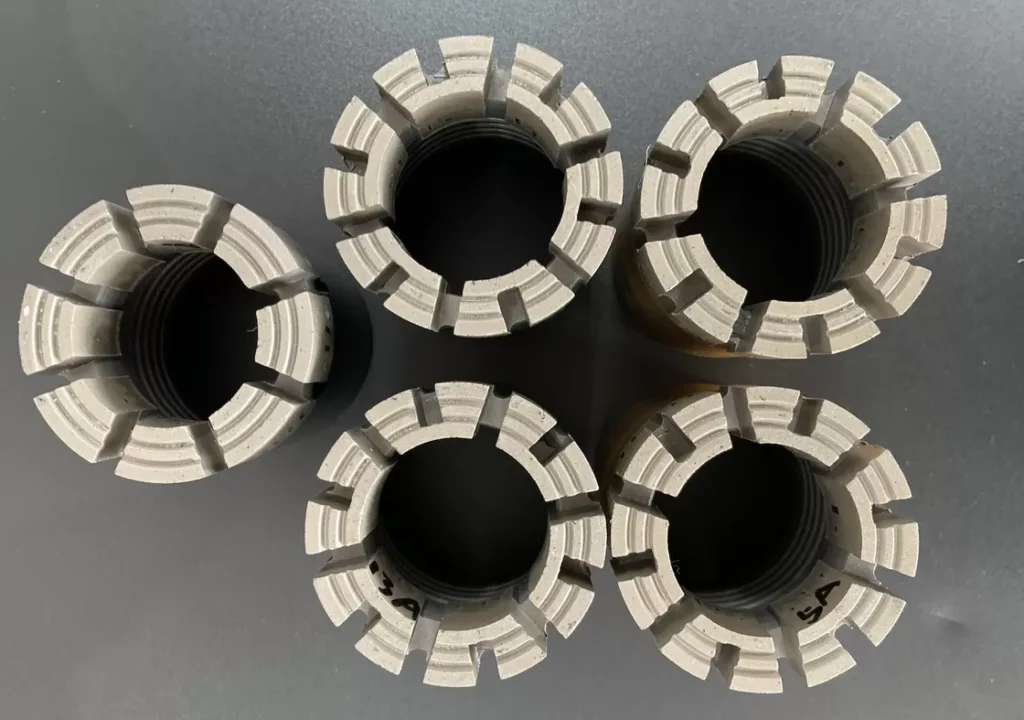
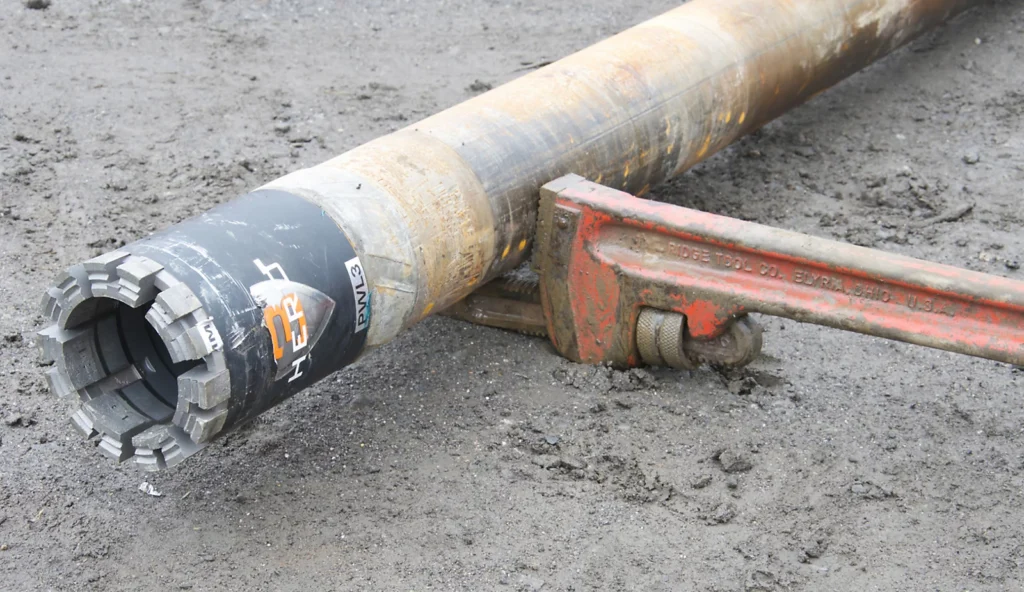
How It Works:
1. Site Setup – We mobilize quickly, ensuring the area is prepped for minimal disruption.
2. Drilling Begins – Our high-performance rigs drill down with diamond-tipped bits.
3. Core Retrieval – We extract continuous samples, stored in trays for inspection.
4. Analysis & Reporting – Cores are logged, analyzed, and interpreted by our experts.
How Much It Costs:
Request A Quote
Why It Matters:
– Critical for mining exploration, geotechnical design, and infrastructure projects
– Can reach up to 1,800m depth with excellent sample quality
Applications of Diamond Core Drilling:
2. Geotechnical Investigations: Assesses soil and rock stability for infrastructure, construction, and foundation projects.
3. Environmental Studies: Supports groundwater assessments and contamination analysis.
4. Mining Operations: Guides excavation planning and resource estimation.
1. High-Quality Sampling: Produces intact core samples that accurately reflect geological formations, enabling precise analysis of rock properties and mineral content.
2. Efficiency & Depth Capability: Can reach depths of up to 1,800 meters while maintaining speed and accuracy, making it ideal for deep exploration projects.
3. Low Environmental Impact: Generates minimal noise, vibration, and waste compared to traditional drilling methods, reducing ecological disruption.
4. Cost-Effective Exploration: Reduces overall project costs by optimizing exploration time and improving resource evaluation accuracy.




How It Works:
1. Borehole Drilling – We drill to the required test depth.
2. Sampler Insertion – A split-barrel sampler is driven into the soil with a 63.5kg hammer.
3. Blow Count Recorded – We count the number of hammer blows for penetration.
4. Results Delivered – The N-values are analyzed for soil classification and bearing capacity.
How Much It Costs:
Request A Quote
Why It Matters:
– Assesses potential for settlement or liquefaction
– Simple, reliable, and industry-accepted
Applications of SPT:
2. Soil classification and strength estimation
3. Liquefaction potential assessment in seismic-prone areas
4. Correlation with other geotechnical parameters for subsurface profiling
The test involves driving a 50mm diameter split-barrel sampler into the soil using a 63.5kg hammer, which is dropped from a height of 760mm. The sampler is driven in six 75mm increments, with the number of blows recorded for the final 300mm penetration—this value is known as the SPT “N-value”. The initial 150mm penetration is disregarded to account for soil disturbance caused by the boring process.
In cases where 50 blows are insufficient to drive the sampler the full 300mm, the penetration depth at 50 blows is recorded.
Sampling & Interpretation
1. Cohesive Soils (Clay & Silt): A disturbed sample is collected inside the split-barrel sampler for visual classification. For more detailed engineering analysis, undisturbed samples are required to determine properties like shear strength and compressibility.
2. Granular Soils (Sand & Gravel): When testing below the groundwater table, N-values may underestimate the actual density. In such cases, additional penetration beyond the standard test depth can provide further insight into soil conditions.
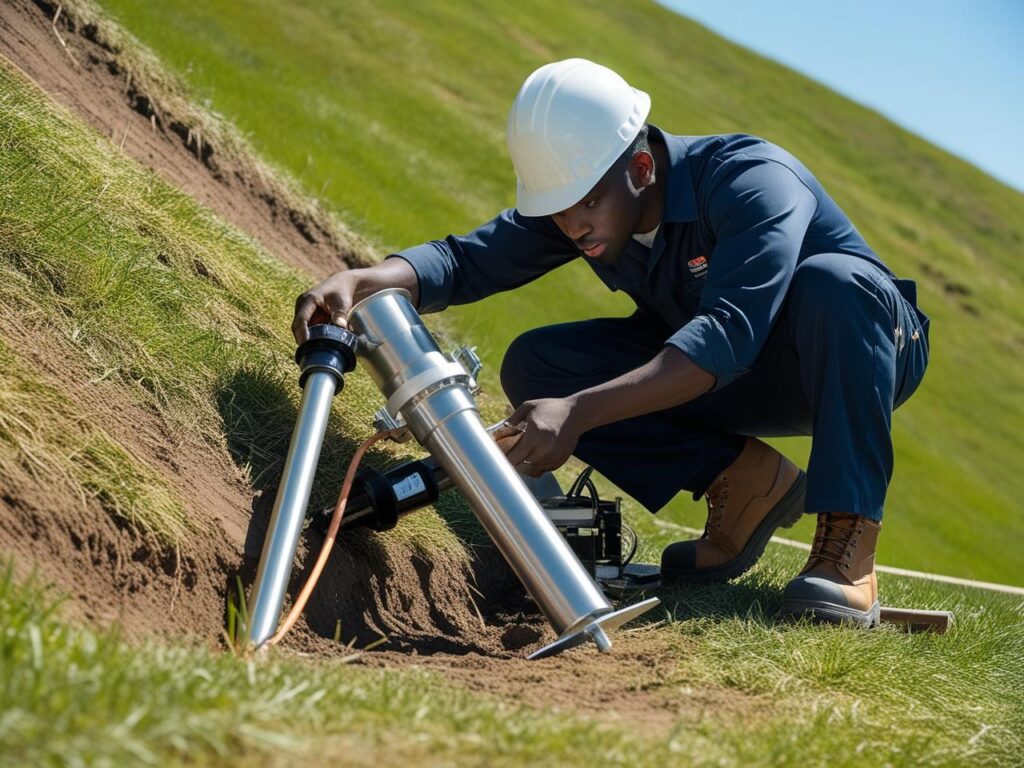




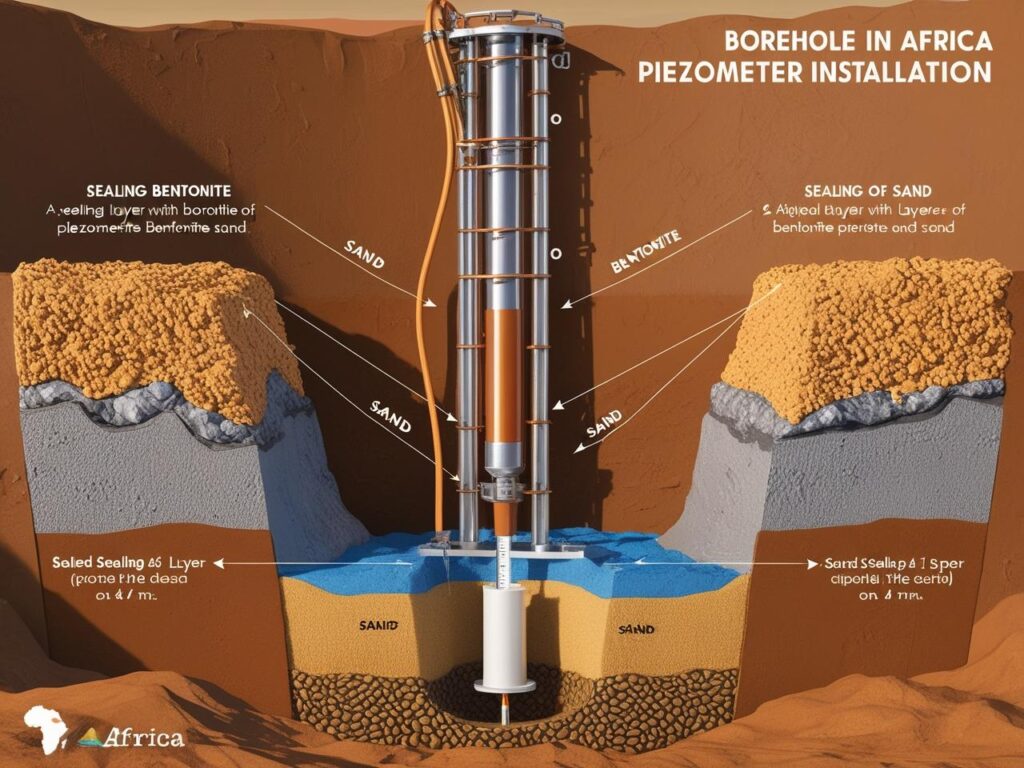
How It Works:
1. Borehole Drilling – We drill to the exact target depth.
2. Filter & Pipe Placement – A porous filter pipe is positioned and surrounded with sand.
3. Sealing – Bentonite and grout seal the borehole to prevent contamination.
4. Monitoring – Water levels rise in the pipe, indicating pore water pressure.
How Much It Costs:
Request A Quote
Why It Matters:
– Supports slope stability and dam safety assessments
– Essential for dewatering and environmental impact analysis
Applications of Piezometer Installation:
2. Assessing slope stability and landslide risk
3. Evaluating the effectiveness of dewatering systems
4. Monitoring pore water pressures in tailings dams and embankments
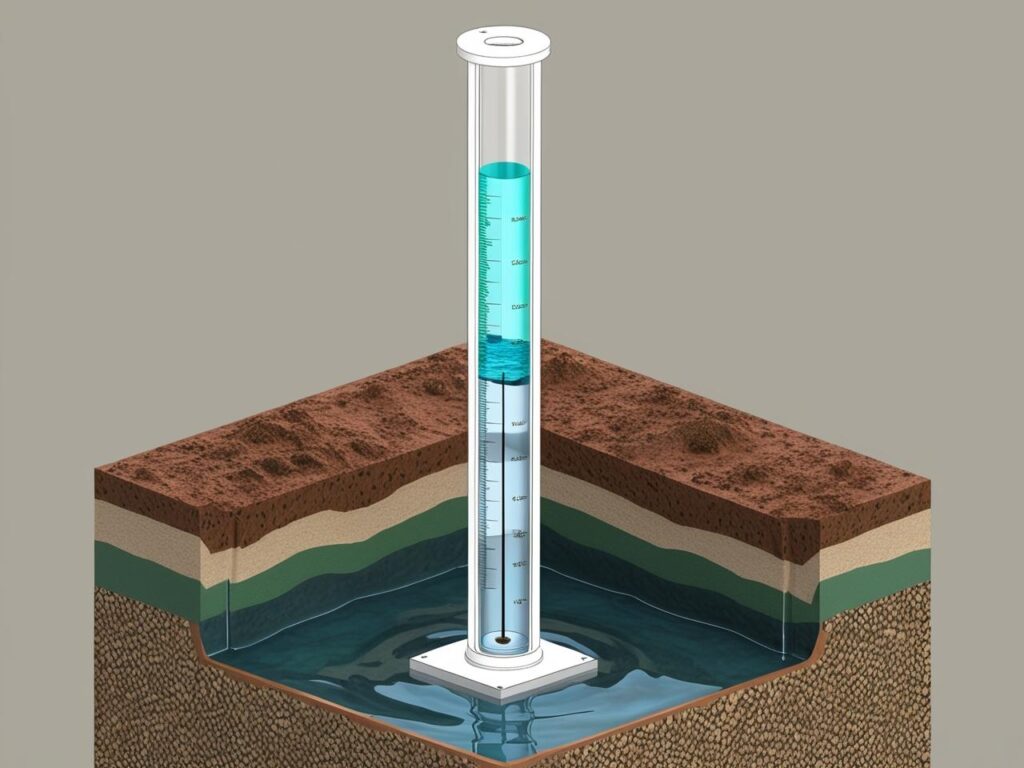
Groundwater pressure causes water to enter the standpipe and rise to a level that corresponds to the pore water pressure at the filter depth. By monitoring this water level over time, engineers can assess groundwater fluctuations, soil drainage conditions, and potential stability concerns.



How It Works:
1. Desktop Study – We review maps, past data, and geology.
2. Field Drilling & Testing – Core drilling, SPT, and sampling on-site.
3. Lab Analysis – Samples tested for strength, density, moisture, etc.
4. Geotechnical Report – Comprehensive insights to guide your design.
How Much It Costs:
Request A Quote
Why It Matters:
– Ensures regulatory compliance
– Reduces long-term construction risks
Applications of Geotechnical Site Investigations:
2. Residential & Commercial Developments
3. Roads, Bridges & Transportation Infrastructure
4. Dams, Embankments & Slopes
5. High-Rise & Industrial Construction
6. Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs)
7. Underground Utilities & Tunnels
8. Groundwater & Dewatering Planning
9. Slope Stability Analysis
10. Retaining Structure Design
11. Pavement Design
12. Earthworks & Excavation Planning
13. Seismic Hazard Assessment
14. Site Classification for Building Codes
15. Landfill and Waste Facility Siting





